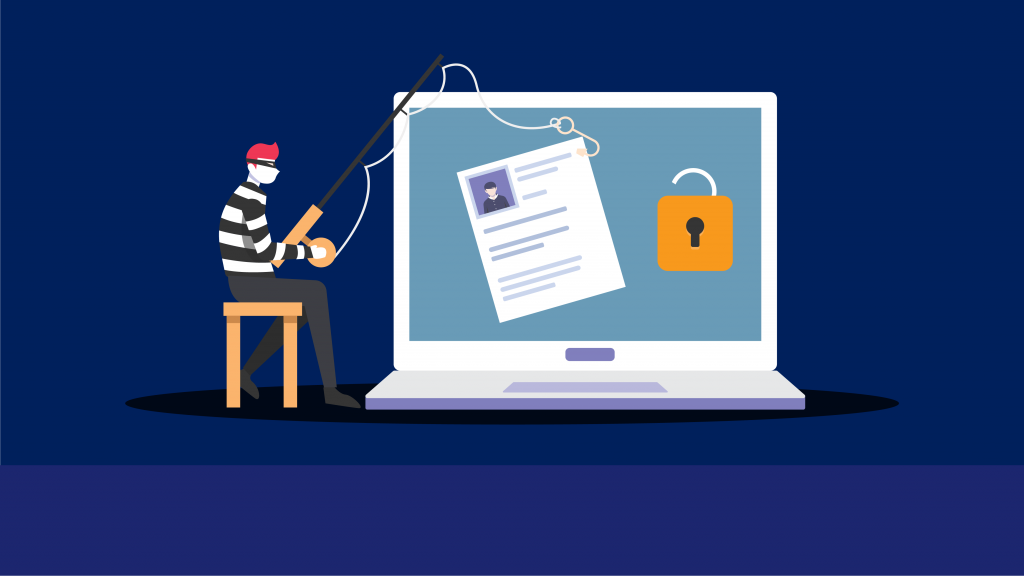
What are Phishing Attacks?
Phishing attacks are a type of cyber attack that uses fraudulent emails, messages, or websites to trick individuals or organizations into divulging sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal data. The attackers often impersonate a reputable source, such as a bank or an online service provider, to gain the victim’s trust and prompt them to take immediate action, such as clicking on a link or downloading an attachment. Once the victim takes the requested action, the attackers can use the information to gain access to the victim’s accounts, steal their money, or commit other forms of identity theft.
How Do Phishing Attacks Work?Phishing attacks typically work by exploiting the trust that people have in reputable organizations. The attackers will often create a convincing email or message that appears to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank, social media platform, or online retailer. The message may contain a sense of urgency or fear, such as a warning that the recipient’s account has been compromised, and they need to take immediate action to avoid further damage. The message may also contain a link to a fake website that looks like the real thing but is designed to steal login credentials, credit card numbers, or other sensitive information. Once the victim enters their information on the fake website, the attackers can use it to gain access to the victim’s accounts, steal their money, or commit other forms of identity theft.
Phishing attacks can have a significant impact on companies:- Financial losses: Phishing attacks can result in financial losses, such as fraudulent transactions or stolen funds. In some cases, attackers may demand a ransom to restore access to the victim’s systems or data.
- Data breaches: Phishing attacks can result in data breaches, which can expose sensitive information, such as customer data, intellectual property, or trade secrets. This can lead to legal liabilities, loss of customer trust, and reputational damage.
- Business disruption: Phishing attacks can disrupt business operations by infecting systems with malware, causing network outages, or locking users out of their accounts. This can result in lost productivity, missed deadlines, and lost revenue.
- Compliance violations: Phishing attacks can lead to compliance violations, such as breach of data protection regulations, breach of contractual obligations, or failure to comply with industry standards. This can result in legal penalties, fines, or other regulatory sanctions.
- Reputational damage: Phishing attacks can damage a company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust, negative media coverage, and damage to brand image. This can result in lost business opportunities and long-term harm to the company’s reputation.
- To mitigate the impact of phishing attacks, companies should implement security measures, such as employee training, anti-phishing software, and multi-factor authentication. Companies should also have an incident response plan in place to minimize the impact of any successful attacks. By taking proactive measures to prevent phishing attacks and responding quickly to any incidents, companies can reduce the risk of financial losses, reputational damage, and other negative impacts.
- Email phishing: This is the most common type of phishing attack and involves the use of fraudulent emails that appear to come from a trusted source. The email usually contains a link to a fake website that looks like the legitimate one, and the victim is asked to provide their personal information.
- Spear phishing: This type of attack is similar to email phishing, but it targets specific individuals or organizations. The attacker usually uses information gathered from social media or other sources to make the email appear more convincing.
- Smishing: This is a type of phishing attack that is carried out through SMS or text messages. The victim receives a text message containing a link to a fake website, and they are asked to enter their personal information.
- Vishing: This type of attack is carried out through phone calls. The attacker pretends to be a representative of a legitimate company, such as a bank or a credit card company, and asks the victim to provide their personal information.
- Clone phishing: This is a type of attack where the attacker creates a fake email that appears to be a legitimate email that the victim has already received. The email usually contains a link to a fake website, and the victim is asked to enter their personal information.
- It is important to be vigilant and cautious when receiving any unsolicited email, SMS, or phone call, and to avoid providing personal information unless you are certain that the request is legitimate.
- Be cautious of unsolicited emails, SMS, and phone calls. Don’t click on links or download attachments from unknown sources.
- Verify the authenticity of the sender before providing any personal information. Check the sender’s email address, website URL, or phone number to make sure it is legitimate.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible. 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone.
- Keep your software up to date. Phishing attacks often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software, so keeping your software up to date helps to reduce the risk of an attack.
- Use anti-phishing software. There are several anti-phishing tools available that can help to identify and block phishing attacks.
- Educate yourself on phishing tactics. The more you know about how phishing attacks work, the better equipped you are to recognize and avoid them.
- By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to a phishing attack. It is important to be vigilant and cautious when dealing with any unsolicited communication and to always verify the authenticity of the sender before providing any personal information.